
Consider in case of 8 to 3 line encoder in which, if D2 and D5 are 1 simultaneously, the encoder produces the output as that means all three outputs are equal to logic 1 as an example in case of a person operating keyboard might press a second key before releasing the first. It generates an undefined combination of outputs, if the two inputs are logic 1 simultaneously. Please write comments if you find anything incorrect, or you want to share more information about the topic discussed above.In the previous tutorial we have seen binary encoder s which encode the given data. It is highly recommended that you practice them. All questions have been asked in GATE in previous years or in GATE Mock Tests. Practicing the following questions will help you test your knowledge. Other applications especially for Priority Encoders may include detecting interrupts in microprocessor applications.Encoders are used to translate the decimal values to the binary in order to perform the binary functions such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, etc.Encoders are very common electronic circuits used in all digital systems.
#DECIMAL TO BCD PRIORITY ENCODER K MAP CODE#
Then, the output of encoder will be the ( code corresponding to the active High inputs, which has higher priority. So, to overcome these difficulties, we should assign priorities to each input of encoder.

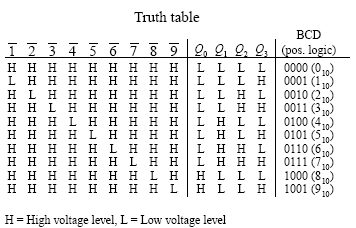
There is an ambiguity, when all outputs of encoder are equal to zero.The above two Boolean functions can be implemented as : The truth table for priority encoder is as follows : In this case, even if more than one input is ‘1’ at the same time, the output will be the (binary) code corresponding to the input, which is having higher priority. Here, the input, Y3 has the highest priority, whereas the input, Y0 has the lowest priority. The above two Boolean functions can be implemented using OR gates :Ī 4 to 2 priority encoder has 4 inputs : Y3, Y2, Y1 & Y0 and 2 outputs : A1 & A0. Logical expression for A3, A2, A1 and A0 : A3 = Y9 + Y8 The truth table for decimal to BCD encoder is as follows: The figure below shows the logic symbol of decimal to BCD encoder : This encoder accepts the decoded decimal data as an input and encodes it to the BCD output which is available on the output lines. Each input line corresponds to the each decimal digit and 4 outputs correspond to the BCD code. The decimal to binary encoder usually consists of 10 input lines and 4 output lines. The above two Boolean functions A2, A1 and A0 can be implemented using four input OR gates : The truth table for 8 to 3 encoder is as follows : The figure below shows the logic symbol of octal to binary encoder: Each input line corresponds to each octal digit and three outputs generate corresponding binary code. The 8 to 3 Encoder or octal to Binary encoder consists of 8 inputs : Y7 to Y0 and 3 outputs : A2, A1 & A0. The above two Boolean functions A1 and A0 can be implemented using two input OR gates : Logical expression for A1 and A0 : A1 = Y3 + Y2 The Truth table of 4 to 2 encoder is as follows : The figure below shows the logic symbol of 4 to 2 encoder : At any time, only one of these 4 inputs can be ‘1’ in order to get the respective binary code at the output. The 4 to 2 Encoder consists of four inputs Y3, Y2, Y1 & Y0 and two outputs A1 & A0. Therefore, the encoder encodes 2^n input lines with ‘n’ bits. It will produce a binary code equivalent to the input, which is active High. An Encoder is a combinational circuit that performs the reverse operation of Decoder.It has maximum of 2^n input lines and ‘n’ output lines, hence it encodes the information from 2^n inputs into an n-bit code.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
